Input and Output
- Introduction to Console I/O function
- Types of Console I/O functions
- Formatted Input Function
-
- scanf()
- Formatted Output Function
-
- printf()
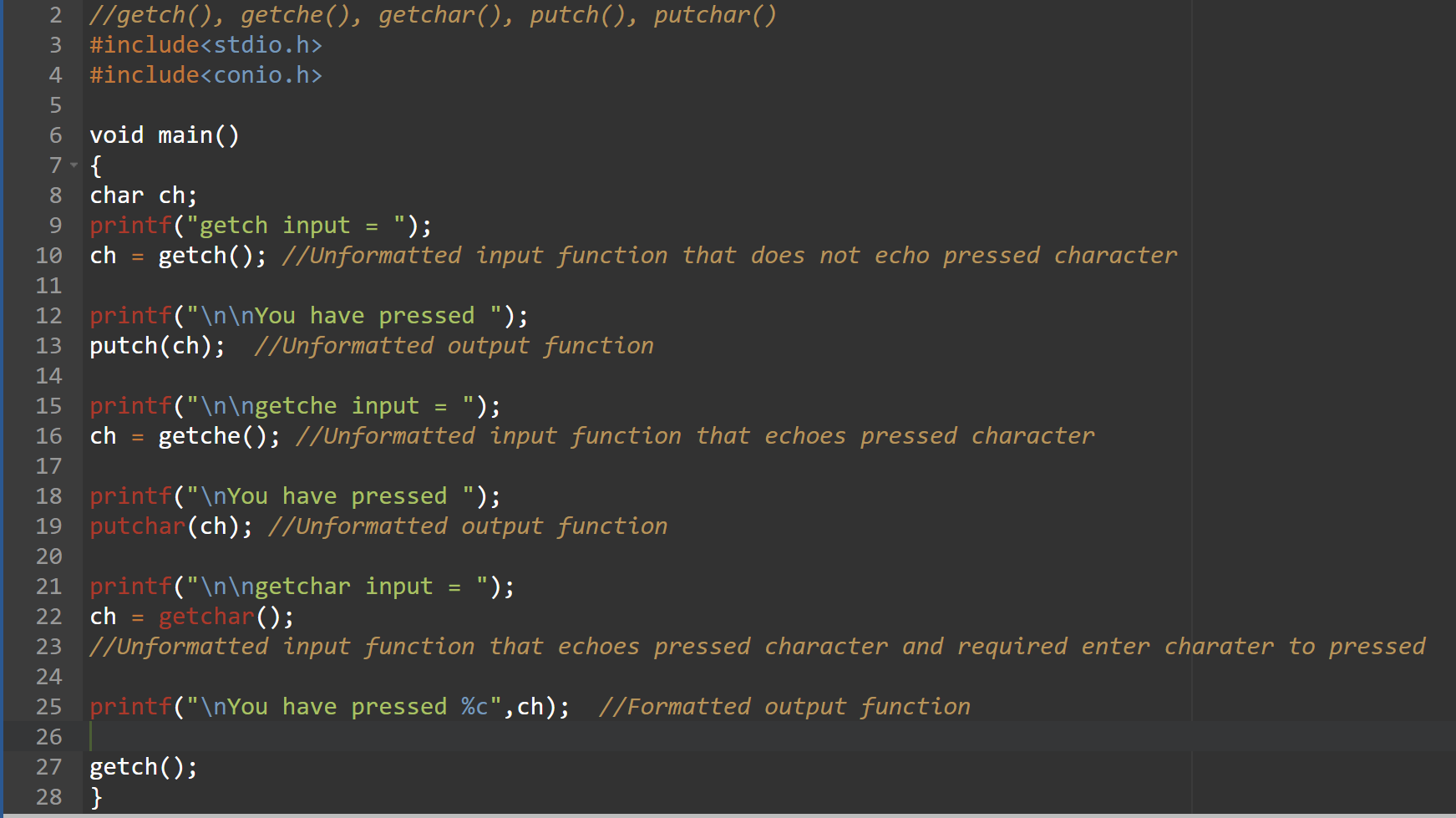
- Unformatted Input functions
-
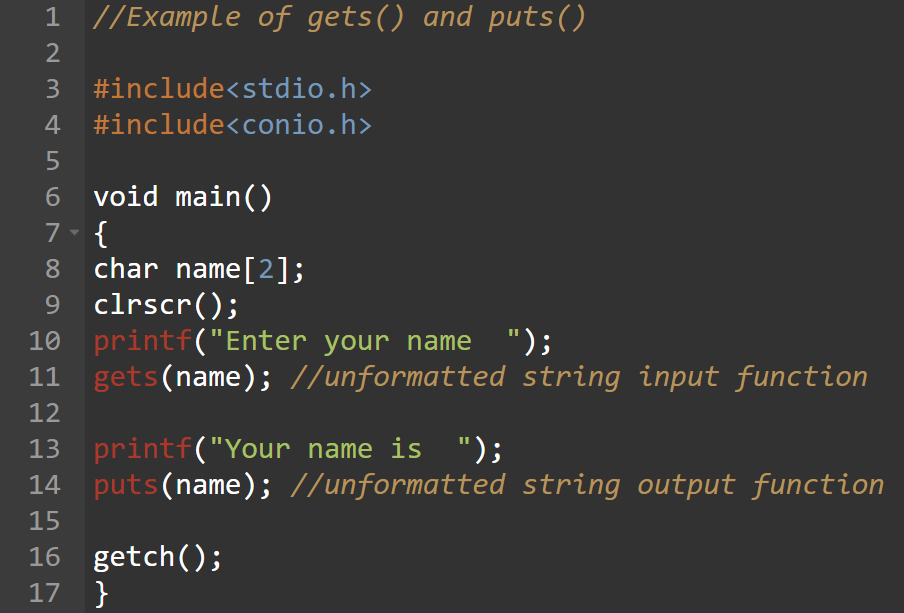
- gets
- getch()
- getche()
- getchar()
- Unformatted Output functions
-
- puts
- putch()
- putche()
- putchar()
Assignment Set
- What are the standard input and output devices? Why are gets and puts function used?
- Why is formatted output required? Write a general format of specification of printing different data types?
- What is the main limitation of scanf() function to read strings?
Board Exam Theory Questions
- What are the differences between formatted and unformatted Input/output. Give suitable example with sample output for the following: %10i, %3c, %-10.3f and %x. [1+4] [2072]
- Define and write syntax of the following: [4] [2072]
i. gets()
ii. putchar()
iii. scanf()
iv. strlen() - Write syntax example and use of following. [1+4] [2071]
i. printf()
ii. scanf()
iii. getche()
iv. getch() - Write syntx and example of following statements/functions: [1x4] [2071]
i. printf()
ii. getch()
iii. scanf()
iv. long - What are the difference between formatted and unformatted I/O statements? Describe with proper example. [4] [2070]
- Consider a statement
scanf(“%s”,str);
where str is a string variable
In above statement, why ‘&’ symbol is not used? Can we input string with space in this statement? If not, why? [4] [2069] - How formatted input/output can be performed in C? Explain with example. [4] [2068]
- Write a program in C to generate following pattern using unformatted input/output functions only. [5]
Input and Output Functions
Every C program performs three main functions i.e. it accepts data as input, processes data and produces output. Input refers to accepting of data while output refers to the presentation of data. Normally input is accepted from keyboard and output is displayed to screen. Input output operations are most common task in every programming language. C languages has different types of input output functions for input-output operations. Out of different input output operations, in this sections, we mainly focus on formatted and unformatted input output functions.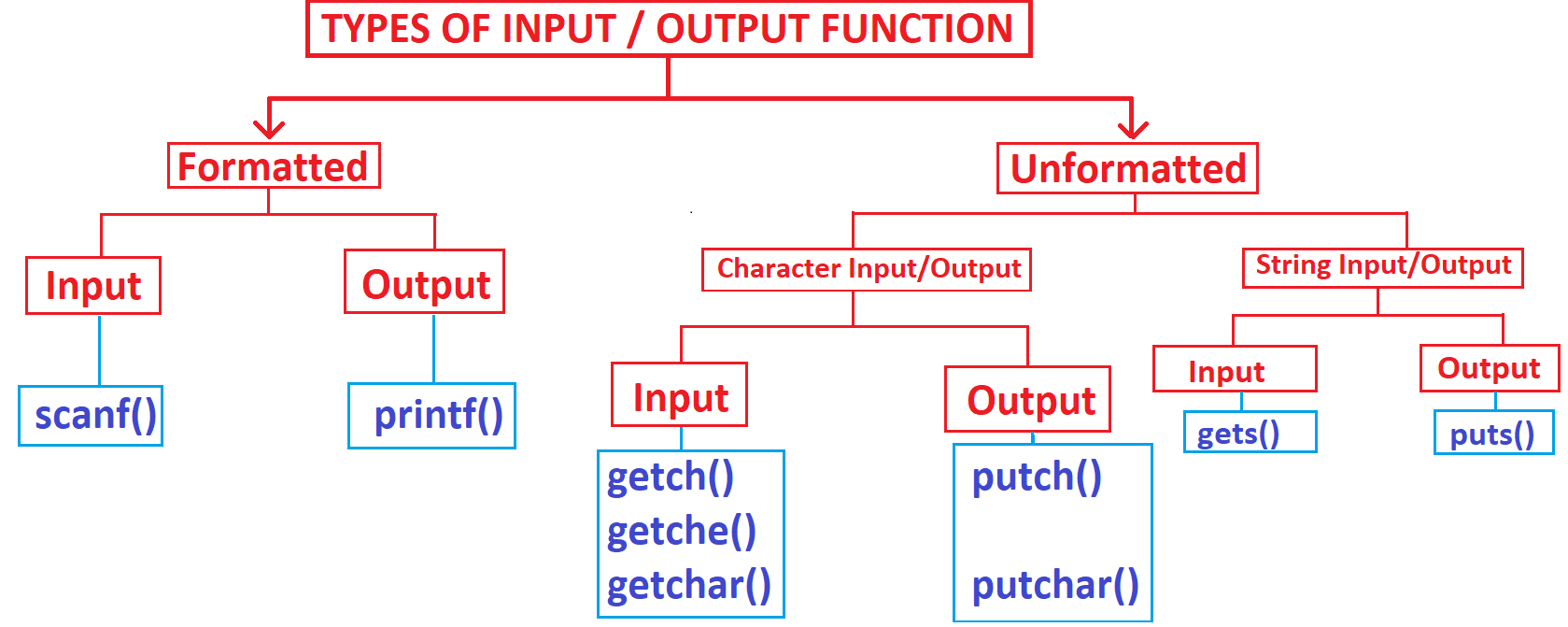
Formatted Input Output Functions
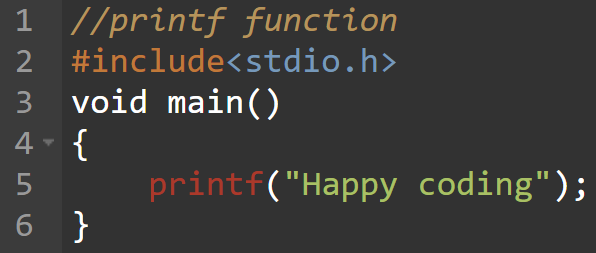
Formatted input output functions accept or present the data in a particular format. The standard library consists of different functions that perform output and input operations. Out of these functions, printf() and scanf() are discussed in this section. These functions allow user to format input output in desired format. printf() and scanf() can be used to read any type of data (integer, real number, character etc).printf() - formatted output function
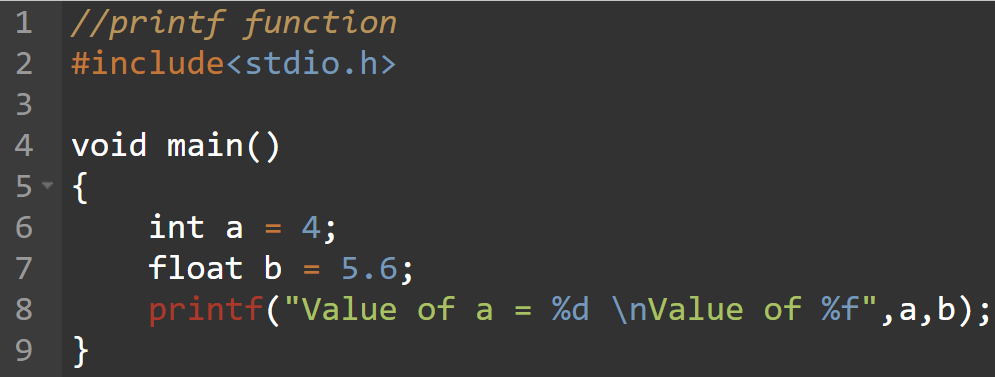
printf() is formatted output function which is used to display some information on standard output device.It is defined in standard header file stdio.h.
So, to use printf(), we must include header file stdio.h in our program.

The format string indicates how many arguments follow and what their types are.
The arguments var1, var2, ... varN are the variables whose values are formatted and printed according to format specifications of the format string.
The arguments must match in number, order and type with the format specifications.
scanf() - formatted input functions
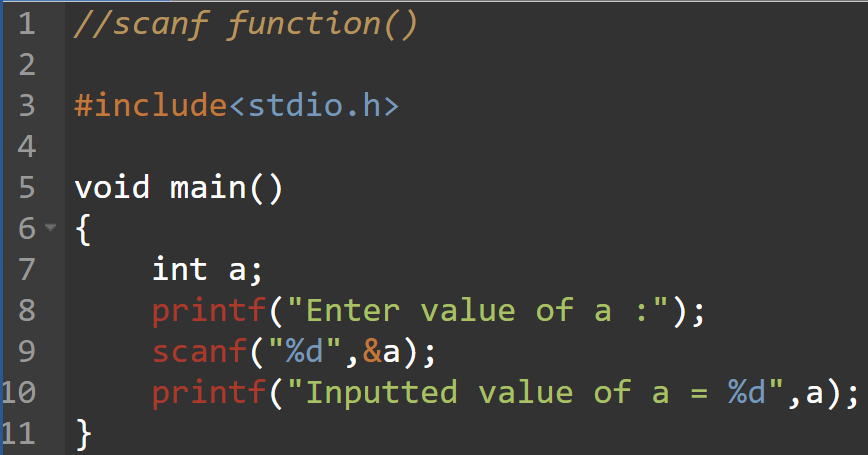
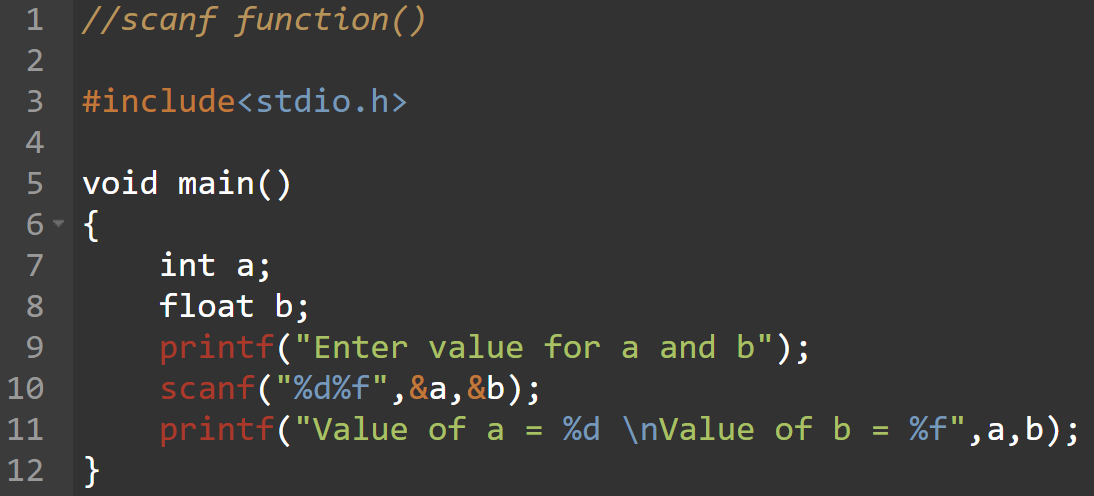
scanf() is formatted input function which is used to read formatted data from standard input device and automatically converts numeric information to integers and floats. It is defined in stdio.h
Unformatted Input Output Functions
Unformatted input output functions cannot control the format of reading and writing the data.Unformatted input output functions are classified into two categories as:
a. Character Input Output functions
Character Input Functions:
i.getch()
getch() is character input functions.It reads a character from the keyboard but does not echo the pressed character which means entered character will not be displayed.
It is defined in header file conio.h
.png)
ii.getche()
getche() is also a character input functions. It reads a character from the keyboard.Difference between getch() and getche() is that getche() echoes pressed character which means entered character will be displayed.
It is defined in header file conio.h.
.png)
iii.getchar()
getchar() is also a character input functions.It reads a character and accepts the input until carriage return is entered (i.e. until enter is pressed).
It is defined in header file stdio.h.
.png)
Character Output Functions:
i.putch()
The putch() function displays alphanumeric characters to the screen.It is defined in header file conio.h .
.png)
ii.putchar()
The putchar() function is also used for displaying alphanumeric characters to the screen.It is defined in header file stdio.h .
.png)
b. String (Collection of Character or Character Array) input output functions
String Input Functions:
gets():
gets() is string input functions.It reads string from the keyboard.
It reads string until enter is pressed.
It is defined in header file stdio.h.
.png)
String Output Functions:
puts():
puts() is string output functions.It writes or prints string to screen.
It is defined in header file stdio.h.
.png)
| S.N. | Formatted Input Output Functions | Unformatted Input Output Functions |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | These functions allow to suppy input or display output in user desired format. | These functions are the most basic form of input and output and they do not allow to supply input or display output in user desired format. |
| 2. | Contain format specifier in their syntax. | Do not contain format specifier in their syntax. |
| 3. | Can be used with many different data type like char, int, float and double. | Can be used with only char or string data type. |
| 4. | They are used for storing data more user friendly. | They are used for storing data more compactly. |
| 5. | printf() and scanf() are examples of formatted input and output functions. | getch(),getche(), getchar(), putch(), putchar(), gets(), puts() are examples of unformatted input output function. |